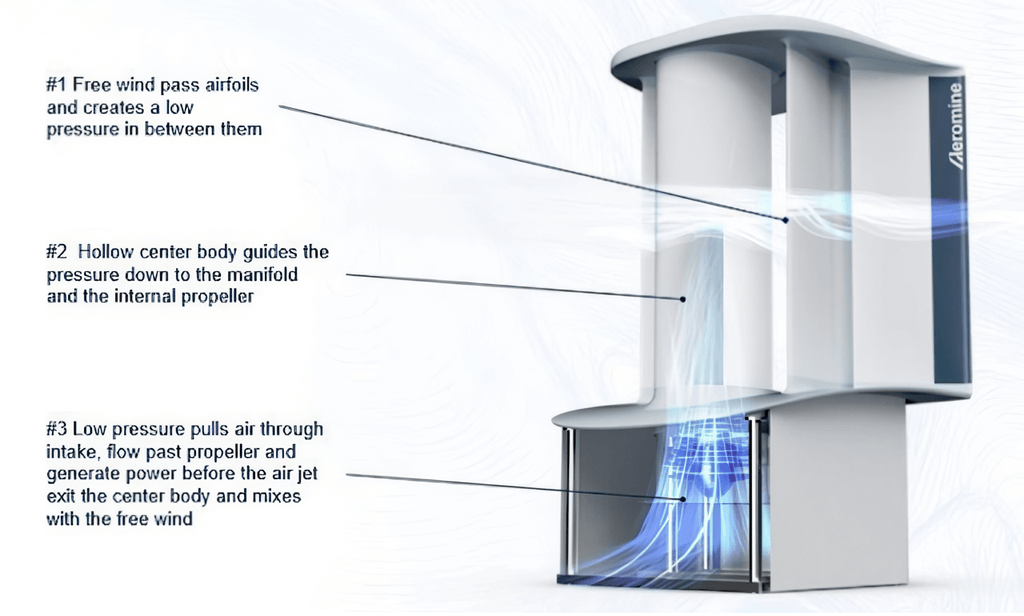
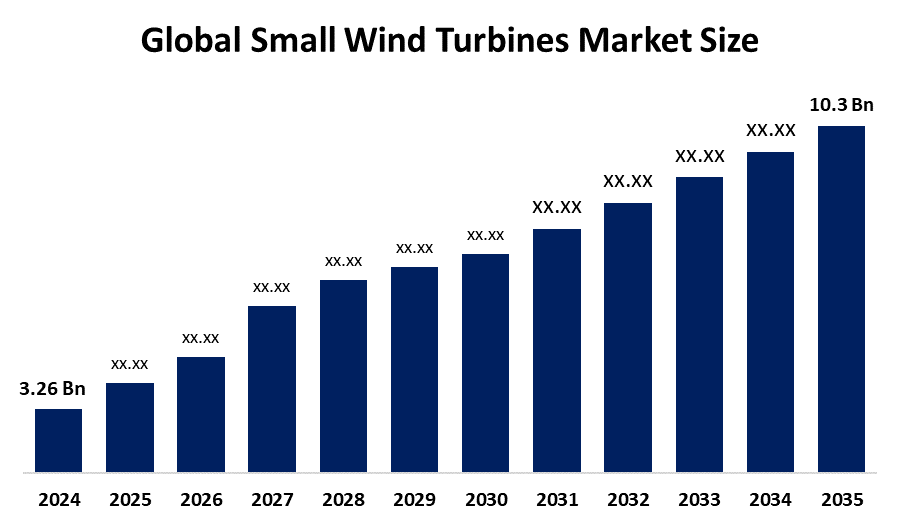
Wind Power
Wind power and wind energy represent one of the most promising and rapidly growing sources of renewable energy in the world today. Wind energy is derived from the natural movement of air in the Earth’s atmosphere, which is converted into electrical power using a rotor connected to a generator. As the rotor spins, it produces electricity that can be distributed through power grids or used locally. Wind energy is clean, sustainable and does not emit greenhouse gases during operation, making it an essential tool in the global fight against climate change.
The use of wind as a source of energy is not new. Ancient civilizations in Persia and China used early windmills for tasks such as grinding grain and pumping water. By the 17th century, Dutch windmills became iconic for their role in agriculture and water management. It was not until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that wind power was first used to generate electricity. The modern wind energy industry began to take shape during the energy crises of the 1970s, when nations sought alternatives to fossil fuels. Since then, advancements in turbine technology, energy storage, and grid integration have made wind power one of the most cost-effective and scalable renewable energy sources available.
There are three primary types of wind energy systems: onshore, offshore, and small-scale. Onshore wind farms are located on land, often in open plains, ridges, or coastal areas where wind speeds are relatively high and consistent. These are the. most common and cost-effective installations. Offshore wind farms, which are built in large bodies of water like seas or oceans, can capture stronger and more stable winds but require greater investment due to construction and maintenance challenges. Small-scale wind systems are used for individual homes, farms or businesses, either as standalone power sources or in hybrid systems with solar panels or battery storage.
Wind energy also offers numerous advantages. It is renewable and virtually inexhaustible relying on the natural circulation of air caused by solar heating of the Earth’s surface. It does not produce any pollution or greenhouse gas emissions during operation, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
“As yet, the wind is an untamed, and unharnessed force; and quite possibly one of the greatest discoveries hereafter to be made, will be taming, and harnessing, or the wind.” - Abraham Lincoln